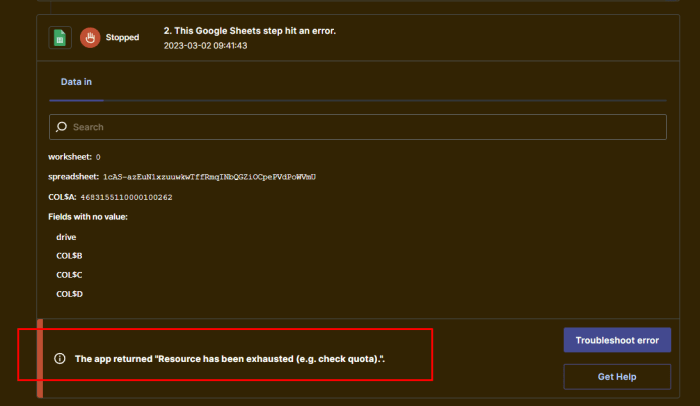
Vicarious liability for employer negligence is a legal doctrine that holds employers responsible for the negligent acts of their employees committed within the scope of their employment. This principle ensures that victims of employee negligence can seek compensation from the employer, even if the employee is not personally liable.
In this article, we will explore the concept of vicarious liability, its scope, and the defenses available to employers in such cases.
The concept of vicarious liability is based on the idea that employers have a duty to control the conduct of their employees and to prevent them from causing harm to others. This duty arises from the employer’s authority over the employee and the employee’s reliance on the employer for direction and supervision.
When an employee commits a negligent act that results in harm to a third party, the employer may be held liable for the employee’s negligence, even if the employer was not directly involved in the act.
Employer Liability for Employee Negligence
Vicarious liability is a legal principle that holds an employer responsible for the negligent acts or omissions of their employees committed within the scope of their employment.
Vicarious liability is based on the idea that employers have a duty to control their employees’ conduct and to prevent them from causing harm to others. This duty arises from the employer’s power to hire, fire, and supervise employees, as well as from the fact that the employer benefits from the employee’s work.
Examples of Vicarious Liability
- A delivery driver who causes an accident while on the job.
- A store employee who negligently injures a customer.
- A doctor who commits malpractice while treating a patient.
Defenses to Vicarious Liability
There are several defenses that employers can assert in vicarious liability cases, including:
- Independent contractor defense:The employee was not an employee but rather an independent contractor.
- Scope of employment defense:The employee’s negligence was not committed within the scope of their employment.
- Employee misconduct defense:The employee’s negligence was intentional or reckless, and the employer did not know or could not have prevented it.
Scope of Employment
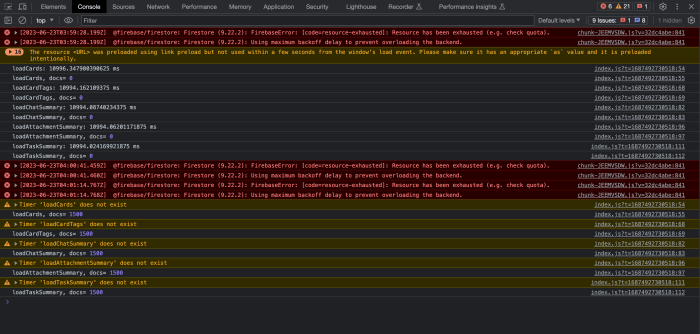
The scope of employment refers to the range of activities an employee is authorized to perform on behalf of their employer. It defines the boundaries within which an employer can be held liable for an employee’s negligent actions.
Determining the scope of employment involves considering several factors, including:
- The employee’s job duties and responsibilities
- The time and place of the employee’s actions
- Whether the employee was acting in furtherance of the employer’s business
Actions Within the Scope of Employment, Vicarious liability for employer negligence
Actions that typically fall within the scope of employment include:
- Performing assigned tasks during work hours
- Attending work-related events or meetings
- Traveling for business purposes
- Using company equipment or property
Actions Outside the Scope of Employment
Actions that typically fall outside the scope of employment include:
- Personal errands or activities
- Criminal acts
- Actions taken after work hours or outside the workplace
- Actions that are not related to the employer’s business
Negligence and Causation: Vicarious Liability For Employer Negligence
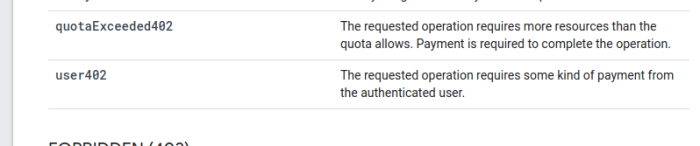
Negligence is a legal concept that refers to the failure to exercise reasonable care, resulting in harm to another person or their property. To establish negligence, the plaintiff must prove four elements:
- Duty of Care:The defendant owed a duty of care to the plaintiff.
- Breach of Duty:The defendant breached their duty of care by acting or failing to act in a way that a reasonable person would not have.
- Causation:The defendant’s breach of duty caused the plaintiff’s injuries or damages.
- Damages:The plaintiff suffered actual damages as a result of the defendant’s negligence.
In vicarious liability cases, causation is a crucial element to prove. The plaintiff must demonstrate that the employee’s negligence was the proximate cause of the plaintiff’s injuries or damages. Proximate cause means that the employee’s actions were a substantial factor in causing the plaintiff’s harm and that the harm was a foreseeable consequence of the employee’s negligence.Proving negligence and causation in vicarious liability cases can be challenging.
However, there are several ways to do so, including:
- Direct Evidence:Witnesses may testify that they saw the employee acting negligently and that the employee’s actions caused the plaintiff’s injuries or damages.
- Circumstantial Evidence:The plaintiff may present evidence of the employee’s negligence and the plaintiff’s injuries or damages, and the jury may infer that the employee’s negligence caused the plaintiff’s harm.
- Expert Testimony:An expert witness may testify about the standard of care for employees in similar situations and whether the employee breached that standard of care.
By presenting evidence of negligence and causation, the plaintiff can establish a strong case for vicarious liability against the employer.
Final Conclusion
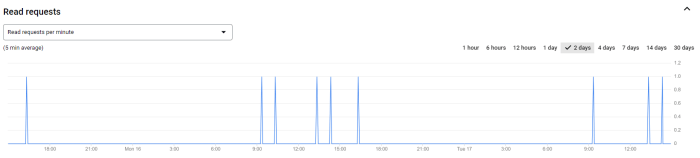
In conclusion, vicarious liability for employer negligence is a complex legal doctrine that can have significant implications for both employers and employees. Employers must be aware of their duty to control the conduct of their employees and to take steps to prevent them from causing harm to others.
Employees must also be aware of the potential consequences of their actions and the fact that their negligence can result in liability for their employer.
User Queries
What is vicarious liability?
Vicarious liability is a legal doctrine that holds employers responsible for the negligent acts of their employees committed within the scope of their employment.
When can an employer be held liable for an employee’s negligence?
An employer can be held liable for an employee’s negligence if the employee was acting within the scope of their employment and the negligence caused harm to a third party.
What are the defenses available to employers in vicarious liability cases?
Employers may have several defenses available to them in vicarious liability cases, including the employee was not acting within the scope of their employment, the employee’s negligence was not the proximate cause of the plaintiff’s injuries, or the plaintiff was contributorily negligent.